News
Customize Battery Packs: Series and Parallel Choices
Understanding Series and Parallel Battery Fundamentals
When we set out to design power solutions for industrial equipment, getting a firm grasp on the relationship between voltage and capacity is super important. Let's talk about series connections first. With series connections, the total voltage goes up while the capacity stays the same. This makes them a great fit for high - power medical devices or communication systems. These kinds of devices need to operate stably even under heavy loads. On the other hand, parallel configurations boost the overall capacity without changing the voltage levels. That’s why they’re the preferred choice for backup power systems in data centers or environmental monitoring devices, where having an extended runtime is really crucial.
Performance Implications of Different Configurations
Now that we’ve understood the basic differences between series and parallel connections, it’s important to note that the thermal management challenges are quite different for these two setups. When cells are stacked in series, during rapid charging cycles, there’s a tendency for uneven temperature distribution. To deal with this, we need advanced heat dissipation solutions. In contrast, parallel configurations face current balancing issues. If these aren’t properly managed with intelligent battery management systems (BMS), it can lead to accelerated degradation of the batteries.
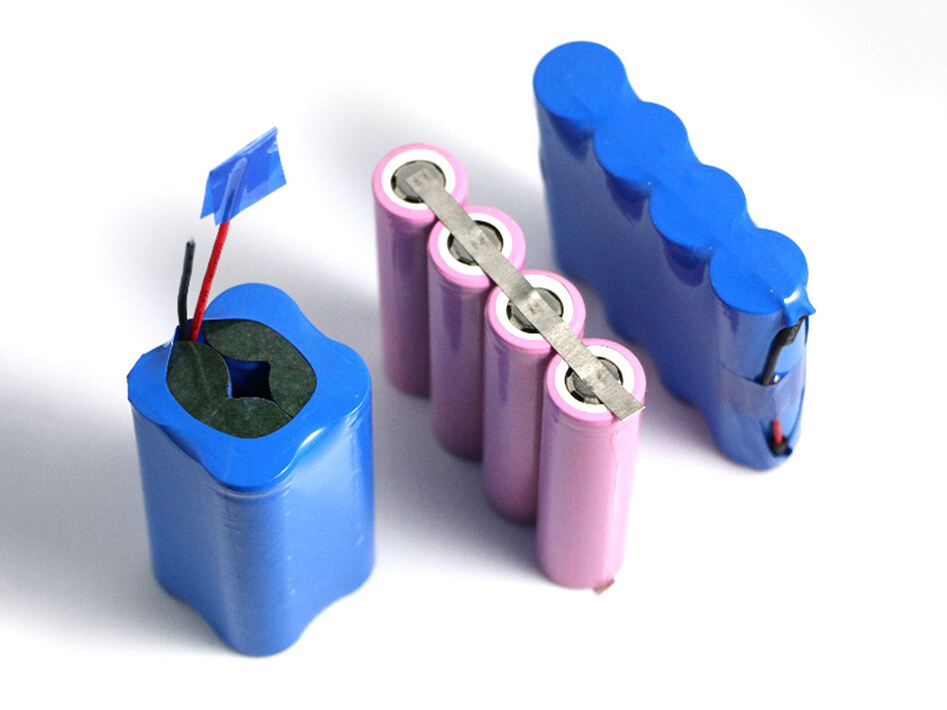

Application-Specific Design Considerations
After looking at the performance implications, we can see that different applications call for different battery configurations. For example, material handling equipment often benefits from hybrid configurations that combine series and parallel connections. This way, it can strike a balance between the need for high torque, which requires voltage, and extended shift durations, which need capacity. When it comes to portable diagnostic instruments, engineers have to focus on space efficiency. At the same time, they must meet strict safety certifications. These factors directly impact the choice of connection methodology and component selection.
Optimizing Battery Pack Longevity
Given the importance of different configurations in various applications, cell matching precision becomes extremely important, especially in large - scale deployments. Industrial applications have strict requirements for voltage tolerances, usually within ±0.5%, and capacity matching within ±1%. This is to prevent reverse charging in series chains or current hogging in parallel arrays. Advanced balancing circuits with active equalization can be a game - changer. Compared to passive balancing systems, they can extend the operational lifespan by 30 - 40%, especially in environments where the temperature fluctuates a lot.
Safety Protocols for High-Density Configurations
Since optimizing battery longevity is crucial, we also can’t overlook safety, especially when dealing with high - density configurations. When stacking cells in series beyond 48V systems, multi - layer protection mechanisms are a must. Arc suppression circuits and reinforced isolation barriers help prevent cascade failures in high - voltage applications. For parallel configurations, current - limiting fuses between branches are needed to contain potential thermal runaway incidents. This is especially important when using high - energy - density lithium chemistries.
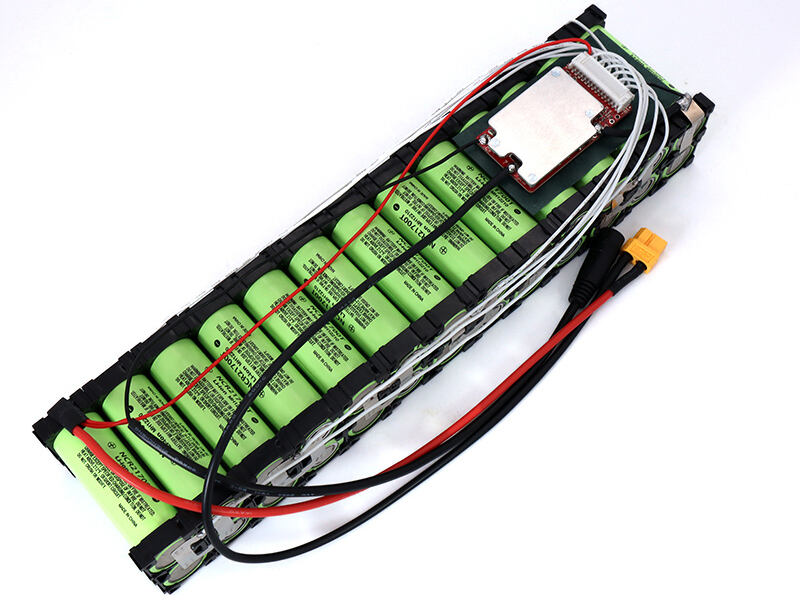
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Industrial Applications
While safety and longevity are key, cost is also a major consideration for industrial applications. Series configurations generally reduce the wiring complexity for high - voltage systems. However, they increase the costs of the BMS because they require more sophisticated voltage monitoring. Parallel setups, on the other hand, offer redundancy advantages. But they need higher - grade busbars to handle the increased current loads. When doing a lifecycle cost modeling, we should take into account the maintenance frequency, the expected cell replacement cycles, and the potential downtime costs specific to each industry.


